1.
Allegory: a tale in prose or verse in which
characters, actions, or settings represent abstract ideas or moral qualities; a
story that uses symbols to make a point
2.
Alliteration: the repetition of similar initial
sounds, usually consonants, in a group of words
3. Allusion: a reference to a person, a place, an
event, or a literary work that a writer expects a reader to recognize
4.
Ambiguity: something uncertain as to
interpretation
5.
Anachronism: something that shows up in the
wrong place or the wrong time
6.
Analogy: a comparison made between two things to
show the similarities between them
7.
Analysis: a method in which a work or idea is
separated into its parts, and those parts given rigorous and detailed scrutiny
8.
Anaphora: a device or repetition in which a word
or words are repeated at the beginning of two or more lines, phrases, clauses,
or sentences
9.
Anecdote: a very short story used to illustrate
a point
10. Antagonist:
a person or force opposing the protagonist in a drama or narrative
11. Antithesis:
a balancing of one term against another for emphasis or stylistic effectiveness
12. Aphorism:
a terse, pointed statement expressing some wise or clever observation about
life
13. Apologia:
a defense or justification for some doctrine, piece of writing, cause, or
action; also apology
14. Apostrophe:
a figure of speech in which an absent or dead person, an abstract quality, or
something inanimate or nonhuman is addressed directly
15. Argument(ation):
the process of convincing a reader by proving either the truth or the falsity
of an idea or proposition; also, the thesis or proposition itself
16. Assumption:
the act of supposing, or taking for granted that a thing is true
17. Audience:
the intended listener or listeners
18. Characterization:
the means by which a writer reveals a character’s personality
19. Chiasmus:
a reversal in the order off words so that the second half of a statement
balances the first half in inverted word order
20. Circumlocution:
a roundabout or evasive speech or writing, in which many words are used but a
few would have served
21. Classicism:
art, literature, and music reflecting the principles of ancient Greece and
Rome: tradition, reason, clarity, order, and balance
22. Cliché:
a phrase or situation overused within society
\
23. Climax:
the decisive point in a narrative or drama; the pint of greatest intensity or
interest at which plot question is answered or resolved
24. Colloquialism:
folksy speech, slang words or phrases usually used in informal conversation
25. Comedy:
originally a nondramatic literary piece of work that was marked by a happy
ending; now a term to describe a ludicrous, farcical, or amusing event designed
provide enjoyment or produce smiles and laughter
26. Conflict:
struggle or problem in a story causing tension
27. Connotation:
implicit meaning, going beyond dictionary definition
28. Contrast:
a rhetorical device by which one element (idea or object) is thrown into
opposition to another for the sake of emphasis or clarity
29. Denotation:
plain dictionary definition
30. Denouement
(pronounced day-new-mahn): loose ends tied up in a story after the climax,
closure, conclusion
31. Dialect:
the language of a particular district, class or group of persons; the sounds,
grammar, and diction employed by people distinguished from others.
32. Dialectics:
formal debates usually over the nature of truth.
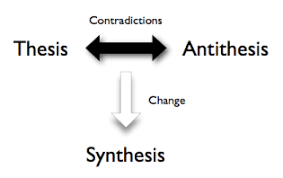
33. Dichotomy:
split or break between two opposing things.

34. Diction:
the style of speaking or writing as reflected in the choice and use of words.
35. Didactic:
having to do with the transmission of information; education.
36. Dogmatic:
rigid in beliefs and principles.

37. Elegy:
a mournful, melancholy poem, especially a funeral song or lament for the dead,
sometimes contains general reflections on death, often with a rural or pastoral
setting.

38. Epic:
a long narrative poem unified by a hero who reflects the customs, mores, and
aspirations of his nation of race as he makes his way through legendary and
historic exploits, usually over a long period of time (definition bordering on
circumlocution).

39. Epigram:
witty aphorism.

40. Epitaph:
any brief inscription in prose or verse on a tombstone; a short formal poem of
commemoration often a credo written by the person who wishes it to be on his
tombstone.

41. Epithet:
a short, descriptive name or phrase that
may insult someone’s character, characteristics
42. Euphemism:
the use of an indirect, mild or vague word or expression for one thought to be
coarse, offensive, or blunt.
43. Evocative
(evocation): a calling forth of memories and sensations; the suggestion or
production through artistry and imagination of a sense of reality.
44. Exposition:
beginning of a story that sets forth facts, ideas, and/or characters, in a
detailed explanation.
45. Expressionism:
movement in art, literature, and music consisting of unrealistic representation of an inner idea or
feeling(s).
46. Fable:
a short, simple story, usually with animals as characters, designed to teach a
moral truth.
47. Fallacy:
from Latin word “to deceive”, a false or misleading notion, belief, or
argument; any kind of erroneous reasoning that makes arguments unsound.
48. Falling
Action: part of the narrative or drama after the climax.
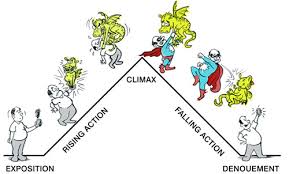
49. Farce:
a boisterous comedy involving ludicrous action and dialogue.

50. Figurative
Language: apt and imaginative language characterized by figures of speech (such
as metaphor and simile).

No comments:
Post a Comment